Rubert Portfolio
Data science and Machine Learning Projects
Inbound tourism in Greece: 2010 - 2020
- collaboration with FrankJKB
- Scrapped inbound tourism information from Government Greece Tourism website.
- Implemented interactive dashboard with Dash and Plotly to show relevant tourism statistics.
- Data cleaning and feature selection with pandas.

Time series forecasting
- collaboration with dgsmith1988 and jansont
- Jointly developed three deep learning architechtures for timeforecsting: Fully connected dense network, LSTM REgressor, Transformer Encoder based model
- Multivariate prediction of weather forecast values. The following image shows the LSTM model prediction and true value for pressure measurements:

- Evaluated each of the proposed models in terms of relevant metrics: MAPE, wMAPE, MDRAE. Results shown in the following table show that the best prediction performance is attained by the Transformer Encoder model

Audio analysis and Spoken language classification
- collaboration with dgsmith1988, maxsolomonhenry, emmanuelwilson and Achaebe for the Final Project of McGill Deep Learning Course ECSE-552
- AutoEncoder reconstrutction of spoken language samples:

- Voice samples extracted from VoxForge and procesed with the librosa library to obtain melSpectrograms.
- Language prediction with three deep learning models commonly utilized on image analysis: ResNet50 pretrained network, AutoEncoder based model and Prototypical Network.
- Three languages (ENglish, ESpagnol and DEutsch) were utilized in the classification task. The following figure shows the obtained confussion matrix for the case of the Prototypical network:

Logistic Regression Classifier
A logistic regression classifier has been implemented in two versions: one based on the method of Loss Minimization through Gradient Descent; the other based on Likelihood Maximization through Gradient Ascent. The algorithms have been applied to two datasets: Hepatitis and Bankruptcy. Different techniques of data analysis have been applied to the data. Experiments have been conducted to determine the balance between accuracy and running time by changing the relative tolerance of the algorithms and the learning rate. Further feature engineering has been applied to the data in order to increase the obtained accuracy of the models
Clothes price prediction
- This project shows an end-to-end implementation of image classification using Convolutional Neural Networks. The input data is a modified version of the FashionMNIST dataset where each image contains three articles and the sum of the prices is the label of the image. The VGG-16 structure was the most accurate amongst other types and was used to train a neural network. The learning rate, the momentum of the optimizer, the number of epochs and the batch sizes hyperparameters were tuned. The optimized values were lr = 10−2, momentum = 0:5, batch_size = 27 and n_epoch = 50 which achieved 96:7% of accuracy on the validation set.
subreddit posts classifier
-
In this project, different Machine Learning Classifiers have been implemented to process text from Reddit and classify each post of the data. Two different Naive Bayes algorithms have been implemented from scratch. In addition, several SciKit-Learn based Machine Learning algorithms have also been used. All these implementations have been compared in terms of accuracy and running time by changing the principal hyperparameters of each one. It is concluded that the best algorithm is Logistic Regression for the given data.
-
The following figure shows the confussion matrix obtained for the classification process:
Fluid dynamics projects
Multiple submerged obstacles (2022)
- Surface waves vs Jetting on a Free surface with multiple obstacles submerged underneath.
- Classification phase map with decision boundary between two fluid regimes: Jetting and Gravity Waves.
Liquid surface profiler (2021)
Created an obstacle detection and surface tracker suite with GUI. Large video processing capabilities. Batch processing of multiple experiments.
[Jetting onset on flow past a cylindrical obstacle - experiments. (2021)]
(research article submitted for revision)
A novel experiment is presented to study the initial disturbances on a free surface due to the constant acceleration of liquid around a submerged obstacle. The surface response to different obstacle sizes, initial surface heights and fluid velocities is measured using high-speed videography. Perturbations observed on the surface are classified into either jetting or gravity waves by measuring the steepness of growing liquid columns. A classification phase map between these two regimes is obtained and compared with analytical results by Martín Pardo and Nedić (2021). The agreement between decision boundaries is good for high Froude numbers (high fluid velocities) but deteriorates at lower velocities, where viscosity and surface tension effects (not considered in the analytical model) have a greater predominance. The surface profile and perturbation amplitude measured in experiments are also compared against this analytical model. In all cases, the model accurately predicts the corresponding experimental results at the beginning of the motion, but the prediction error increases with time. It is also observed that faster moving surfaces that lead to the onset of jetting have greater prediction accuracies and longer validity times of the predictions
Nonlinear surface features:

Surface disturbances on a flow past a cylindrical obstacle (Analytical method)
Published as :Martín Pardo, R., & Nedić, J. (2021). Free-surface disturbances due to the submersion of a cylindrical obstacle. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 926, A1. doi:10.1017/jfm.2021.462
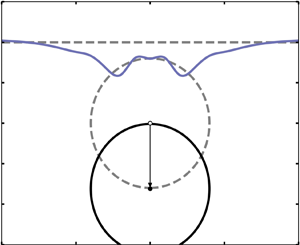
We explore the initial perturbations that form on a liquid free surface as a result of the submersion of a circular cylinder beneath the surface, a scenario that arises in a number of diverse applications. The behaviour of the free surface is determined by transforming the equations of motion of the system via the Wehausen scheme, to variables for the free surface. A small-time series expansion is utilized to construct a recursive scheme that can be implemented numerically, and the time frame over which this approximation is valid is analysed. The resulting numerical model allows one to extend the results in the literature to study arbitrary cylinder sizes, including those where the cylinder is close to the free surface, and arbitrary cylinder motions. Of particular interest in this study was identifying the conditions under which strong jets would appear, and those were the free surface exhibited gravity waves. The formation of a central jet is found to be related to the growth of secondary, nonlinear waves, which rapidly merge as the obstacle is submerged. Classification maps are presented as a function of obstacle size and submersion speed, to identify the conditions which lead to jetting. Furthermore, the acceleration profile of the cylinder is shown to significantly affect the conditions under which jets form, which we argue is due to the rate at which energy is injected into the system.
Graphical abstract:
Nuclear engineering projects
Neutronic - thermal coupling in a real-time nuclear reactor simulator. (2017)
This work presents the characterization and analysis of calculation neutronic library PUMITA, aimed to model the neutronic behavior of nuclear reactor CAREM-25 core. This library will be coupled to the plant analysis code RELAP as the nuclear reactor core model for the Graphical Interactive Simulator aimed at training the future operators of CAREM-25. Thereby is essential for a thorough characterization of the library, to include studies and characterization of the abovementioned coupling as well
Schematic of time stepping strategy for neutronic-thermal coupling

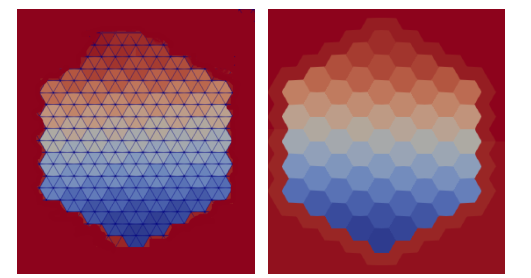
Hexagonal and triangular geometries of core mesh:
Coupling between neutronic code CITVAP and thermal code RELAP for a nuclear reactor (2016)
A coupling method between neutronic code CITVAP and thermal code RELAP is developed for stationary states of the core of a nuclear reactor. Programs relap2citvap y citvap2relap are developed to allow for the information flow between the two codes. The proper functioning of the coupling is validated against experimental data from Australian reactor OPAL. In particular the feedback coefficient is computed, and compared against the measured experimental value. A good agreement between the numerical and experimental values is observed.
Power distribution - OPAL reactor:

Physics projects
Electronic Turing Machine (2012)
Turing Machine is a mathematical model designed to study the limits of computability. This work discusses the physical principles on which this model is based and its viability. In particular, an implementation of an electronic circuit that simulates a Turing Machine is desrcibed in this work. This work was submitted to the XXIX Students Scientific Workshop of the Faculty of Physics of the University of Havana, held on May 16 and 17, 2013.
Preview of the electronic circuit:

Cluster Algorithms (2013)
Metropolis Algorithm (Monte Carlo) has a critical delay when used for simulating the Ising Model near Curie Temperatures (Tc = 2.23K). This work studies the causes of this delay and the main computational algorithms that have been developed to avoid it. Comparisons between different Cluster Algorithms are presented, and against the classical Metropolis Algorithm. Both Swendesn-Wang and Wolff algorithms prove to be more efficient near Tc temperatures than Metropolis.




